
Note 1: This formula is derived from first principles.
Derivative of log a x how to#
See change of base rule to see how to work out such constants on your calculator.)

Then we can obtain the derivative of the logarithm function with base b using: `=2\ cot\ 2x+x/(x^2+1)` Differentiating Logarithmic Functions with Bases other than e Next, we use the following rule (twice) to differentiate the two log terms: It means the same thing.įirst, we use the following log laws to simplify our logarithm expression: We need the following formula to solve such problems. For example, we may need to find the derivative of y = 2 ln (3 x 2 − 1). Example 2. Next, we spell out what it means for exponential and logarithmic functions to be one-to-one. Most often, we need to find the derivative of a logarithm of some function of x. In words: the derivative of the natural log evaluated at a function (g(x)) is the derivative of the inside function (g(x)) divided by the inside function. logb (bx) x for all x and blogb(x) x for all x > 0. Unfortunately, we can only use the logarithm laws to help us in a limited number of logarithm differentiation question types. Derivative of y = ln u (where u is a function of x)
The above graph only shows the positive arm for simplicity. NOTE: The graph of `y=ln(x^2)` actually has 2 "arms", one on the negative side and one on the positive. The graph of `y=ln(x^2)` (in green) and `y=ln(x)` (in gray) showing their tangents at `x=2.` According to the definition of the derivative, we give an increment (Delta x gt 0) to the independent variable (x) assuming that (x + Delta x gt 0).

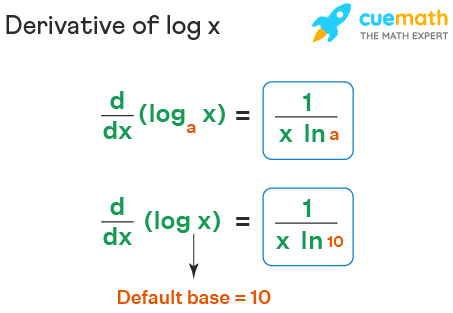
The common logarithmic function is written as ylog10x. The graph on the right demonstrates that as `t->0`, the graph of `y=(1+t)^` is:ġ 2 3 4 5 6 7 -1 1 2 3 -1 -2 -3 -4 x y slope = 1 slope = 1/2 Open image in a new page A function defined by ylogax,x>0, where xay,a>0, a1 is called the logarithm of x to the base a. 1 2 3 4 5 -1 -2 2 4 6 8 10 -2 t y e Open image in a new page


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
